With the number of network equipment grows, data centers are facing the pressure of managing multiple computers and networking devices efficiently. If you need to control multiple computers, you need to buy sets of keyboard, monitor, and mouse. This is not the most effective management considering space-consuming and budget. Also keeping a row of large CRT monitors with keyboards and mouse may be problematic. Thus the KVM switch is invented to solve the problems by monitoring and controlling the devices locally and remotely. So what is a KVM switch? How to use a KVM switch? This article will explain it to you.
What Is A KVM Switch?
The KVM switch is a hardware device that allows users to manage multiple computers from a single keyboard, video display monitor and mouse. By pressing the button on the KVM switch, the administrator can monitoring all the devices locally and remotely. Using KVM switches in data centers not only saves administrators the cost of buying a dedicated keyboard, monitor and mouse for each computer but also saves space in the server room and limit cable clutter. It helps streamlines your work flow and increases your efficiency. Due to its versatile advantages, it is widely used in home offices, laboratories, small and medium-sized enterprises.
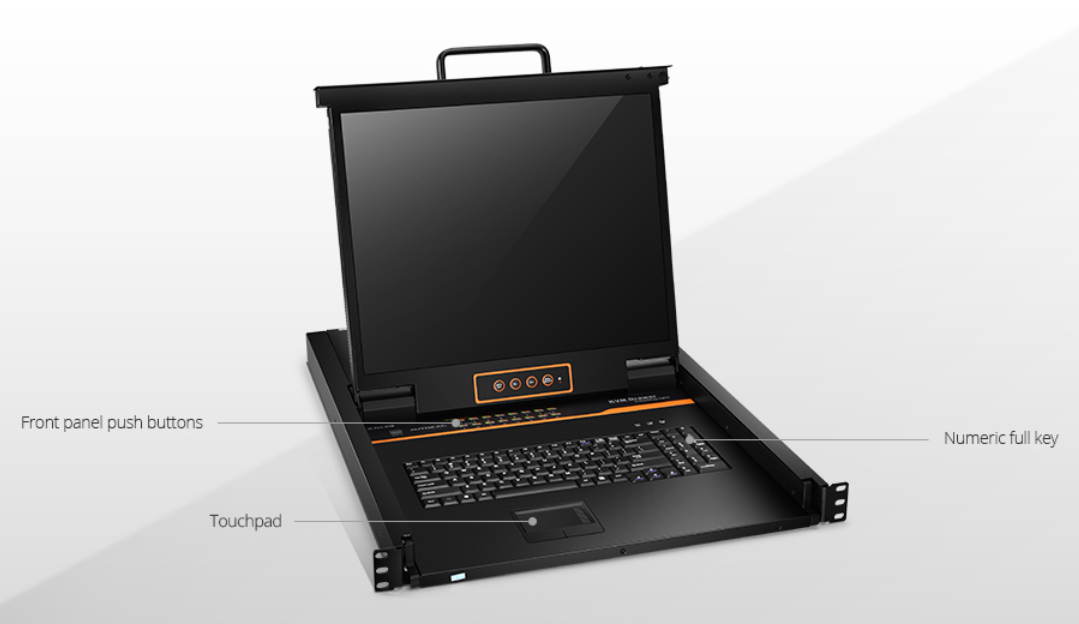

How KVM Switch Works?
The KVM switch can control a number of computers and switch from one computer to another simply by pressing a button on the keyboard. Users can connect their computers to KVM switches via Cat5, Cat5e, and Cat6 patch cables or the specific KVM switch cable kits. Then, connect the keyboard, monitor, and mouse console to the KVM switch. If your switch is equipped with a console, you can skip this step. It mainly uses a keyboard consisting of a keyboard, mouse, and display to securely access computers, servers, and devices from local or remote users, and to control the network for local or remote users.
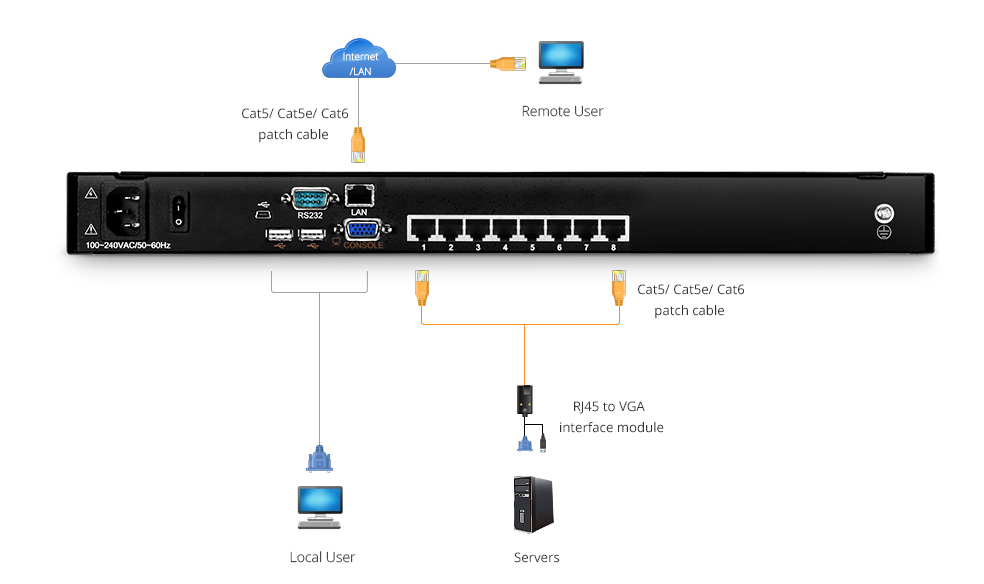
How to Use A KVM Switch?
There are generally three types of switching modes of the KVM switch for us to operate — button switching, OSD menu switching, and shortcut key switching. The button switching is to use the physical button on the KVM, and the corresponding server can be selected by directly pressing the physical button. The OSD menu switching is the KVM internal software. You can use the mouse to select the corresponding server to switch according to the server name displayed on the menu. The shortcut key switching is generally combination keys, such as Ctrl and a data key, 1, 2, 3, 4 four servers, select Ctrl+1 to select the first server, simple and convenient.
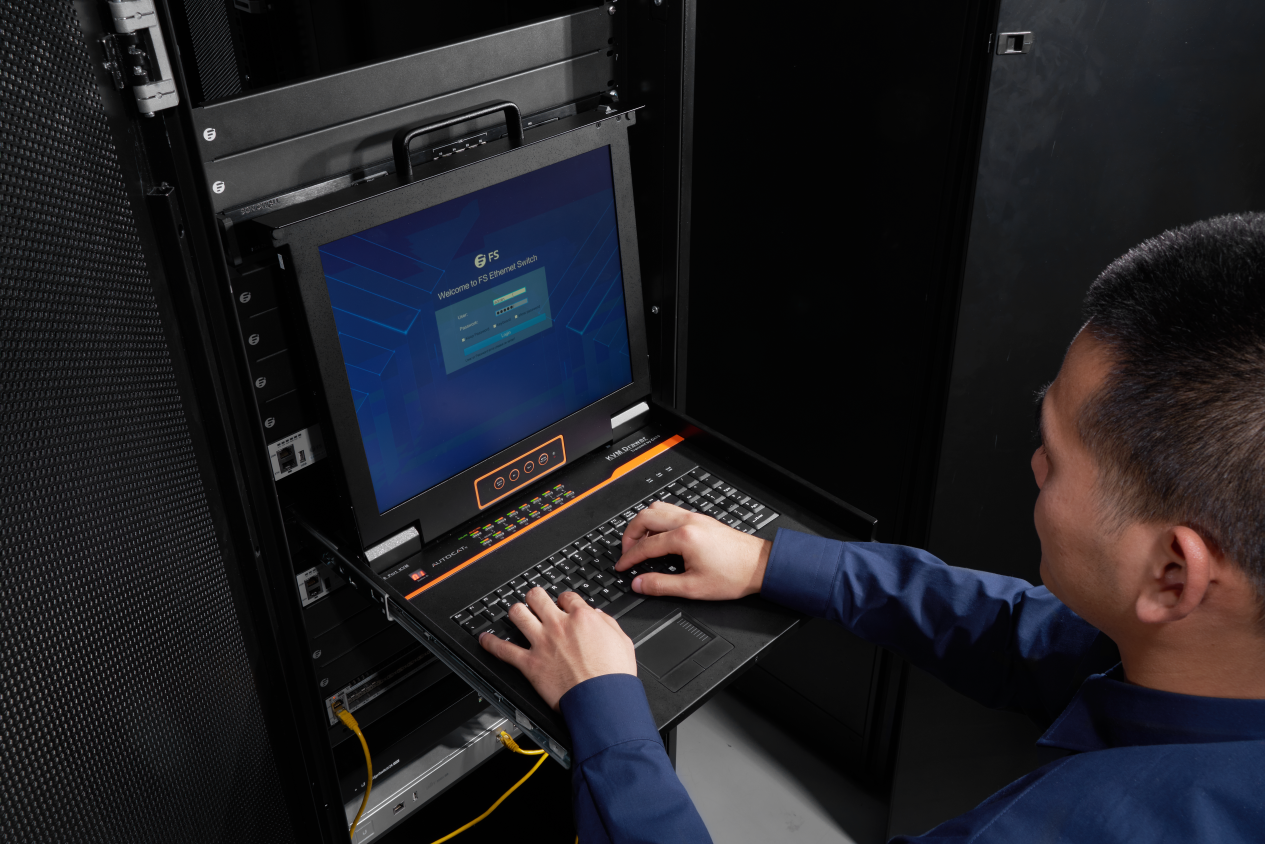

Which KVM Switch to Buy?
When purchasing a KVM switch, the choice usually depends on the number of PCs you need to control. KVM switch with only a few ports is usually more convenient to use without the need to install additional software. They can also be easily managed using hot keys or switch keys. In addition, some of the KVM switches with only a few ports do not even require an external power supply. Due to space needs, advanced KVM switches with multiple ports can be installed in a server rack using only 1U or 2U in space. These KVM switches can also use IP networks to manage power point outlets and control the startup or shutdown of PCs.
Conclusion
KVM switches have become a popular device in data centers with the advantages of space and cost savings, energy efficiency and economy. Thanks for having KVM switches, the server room can be accessed at any time without geographical restrictions. Now that you know how to use a KVM switch and KVM switch buying advice, you can choose a suitable one for your network. FS has high-quality products and professional technical team to provide the ideal solution for your work environment construction. You can have a visit to www.fs.com.
Related Articles:
Questions about KVM Switches You Need to Know
What Is a KVM Switch and How Does It Work?