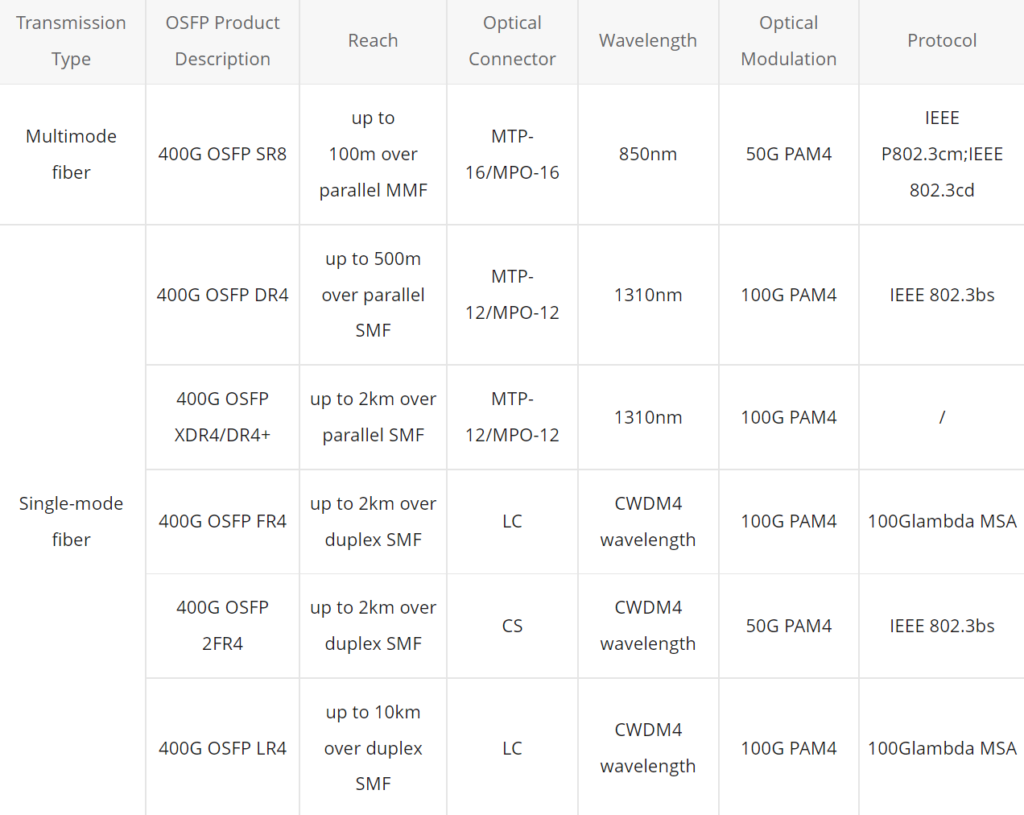
400G ZR and ZR+ coherent pluggable optics have become new solutions for high-density networks with data rates from 100G to 400G featuring low power and small space. Let’s see how the latest generation of 400G ZR and 400G ZR+ optics extends the economic benefits to meet the requirements of network operators, maximizes fiber utilization, and reduces the cost of data transport.
400G ZR & ZR+: Definitions
What Is 400G ZR?
400G ZR coherent optical modules are compliant with the OIF-400ZR standard, ensuring industry-wide interoperability. They provide 400Gbps of optical bandwidth over a single optical wavelength using DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing) and higher-order modulation such as 16 QAM. Implemented predominantly in the QSFP-DD form factor, 400G ZR will serve the specific requirement for massively parallel data center interconnect of 400GbE with distances of 80-120km. To learn more about 400G transceivers: How Many 400G Transceiver Types Are in the Market?
Overview of 400G ZR+
ZR+ is a range of coherent pluggable solutions with line capacities up to 400Gbps and reaches well beyond 80km supporting various application requirements. The specific operational and performance requirements of different applications will determine what types of 400G ZR+ coherent plugs will be used in networks. Some applications will take advantage of interoperable, multi-vendor ecosystems defined by standards body or MSA specifications and others will rely on the maximum performance achievable in the constraints of a pluggable module package. Four categories of 400G ZR+ applications will be explained in the following part.
400G ZR & ZR+: Applications
400G ZR – Application Scenario
The arrival of 400G ZR modules has ushered in a new era of DWDM technology marked by open, standards based, and pluggable DWDM optics, enabling true IP-over-DWDM. 400G ZR is often applied for point-to-point DCI (up to 80km), making the task of interconnecting data centers as simple as connecting switches inside a data center (as shown below).
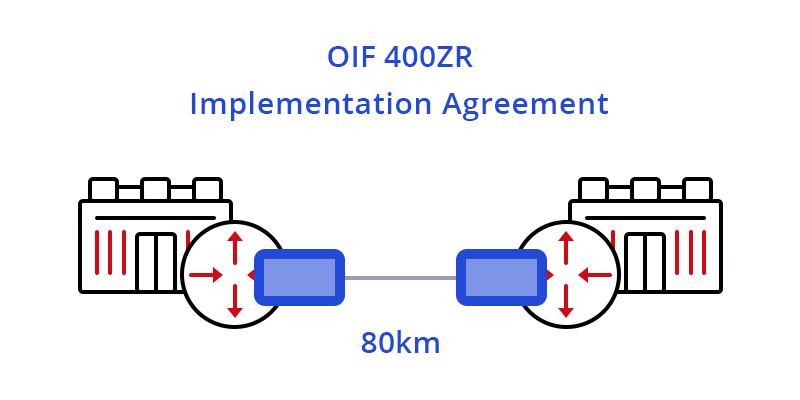
Figure 1: 400G ZR Applied in Single-span DCI
Four Primary Deployment Applications for 400G ZR+
Extended-reach P2P Packet
One definition of ZR+ is a straightforward extension of 400G ZR transcoded mappings of Ethernet with a higher performance FEC to support longer reaches. In this case, 400G ZR+ modules are narrowly defined as supporting a single-carrier 400Gbps optical line rate and transporting 400GbE, 2x 200GbE or 4x 100GbE client signals for point-to-point reaches (up to around 500km). This solution is specifically dedicated to packet transport applications and destined for router platforms.
Multi-span Metro OTN
Another definition of ZR+ is the inclusion of support for OTN, such as client mapping and multiplexing into FlexO interfaces. This coherent pluggable solution is intended to support the additional requirements of OTN networks, carry both Ethernet and OTN clients, and address transport in multi-span ROADM networks. This category of 400G ZR+ is required where demarcation is important to operators, and is destined primarily for multi-span metro ROADM networks.

Figure 2: 400G ZR+ Applied in Multi-span Metro OTN
Multi-span Metro Packet
The third definition of ZR+ is support for extended reach Ethernet or packet transcoded solution that is further optimized for critical performance such as latency. This 400G ZR+ coherent pluggable with high performance FEC and sophisticated coding algorithms supports the longest reach over 1000km multi-span metro packet transport.

Figure 3: 400G ZR+ Applied in Multi-span Metro Packet
Multi-span Metro Regional OTN
The fourth definition of ZR+ supports both Ethernet and OTN clients. This coherent pluggable also leverages high performance FEC and PCS, along with tunable optical filters and amplifiers for maximum reach. It supports a rich feature set of OTN network functions for deployment over both fixed and flex-grid line systems. This category of 400G ZR+ provides solutions with higher performance to address a much wider range of metro/regional packet networking requirements.
400G ZR & ZR+: What Makes Them Suitable for Longer-reach Transmission in Data Center?
Coherent Technology Adopted by 400G ZR & ZR+
Coherent technology uses the three degrees of freedom (amplitude, phase and polarization of light) to focus more data on the wave that is being transmitted. In this way, coherent optics can transport more data over a single fiber for greater distances using higher order modulation techniques, which results in better spectral efficiency. 400G ZR and ZR+ is a leap forward in the application of coherent technology. With higher-order modulation and DWDM unlocking high bandwidth, 400G ZR and ZR+ modules can reduce cost and complexity for high-level data center interconnects.
Importance of 400G ZR & ZR+
400G ZR and 400G ZR+ coherent pluggable optics take implementation challenges to the next level by adding some of the elements for high-performance solutions while pushing component design for low-power, pluggability, and modularity.
Conclusion
Although there are still many challenges to making 400G ZR and 400G ZR+ transceiver modules that fit into the small size and power budget of OSFP or QSFP-DD packages and also achieving interoperation as well the costs and volume targets. With 400Gbps high optical bandwidth and low power consumption, 400G ZR & ZR+ may very well be the new generation in longer-reach optical communications.
Original Source: 400G ZR & ZR+ – New Generation of Solutions for Longer-reach Optical Communications