FS FHD series MPO/MTP cassettes have become a favorable choice for today’s high speed networks and cloud computing in data centers. They enable high bandwidth, high port density, security monitoring, easy cable management and future data rates migration. With the advent of 40/100G network, MPO/MTP cassettes play a more and more important role in fiber optic network. Their importance needs no further explanation. Today, we will unveil the product and learn some ABCs of FS FHD series MPO/MTP cassettes.
What Are FHD Series MPO/MTP Cassettes?
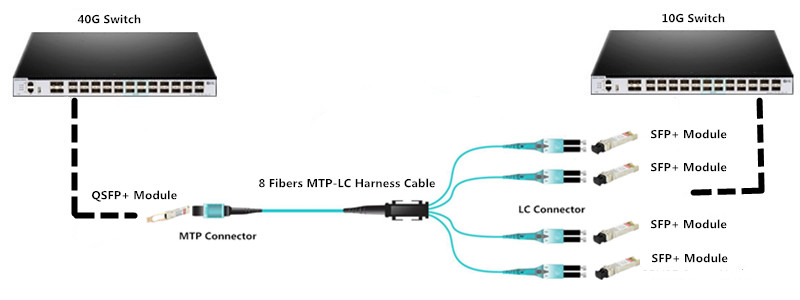
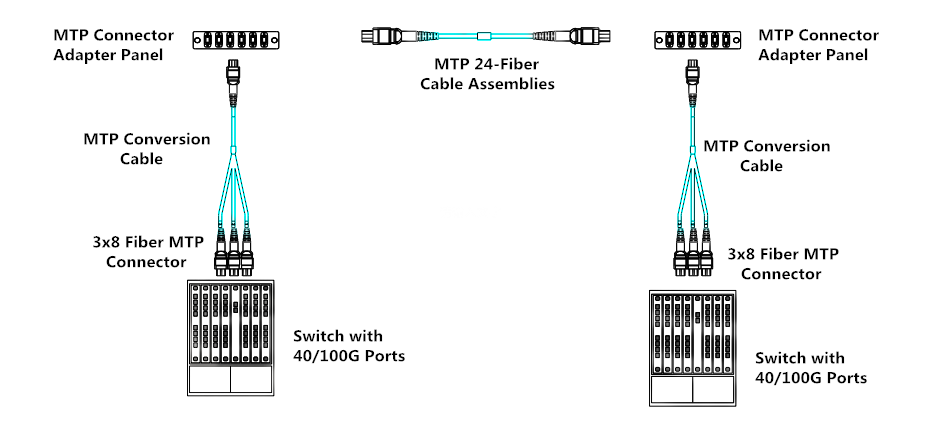
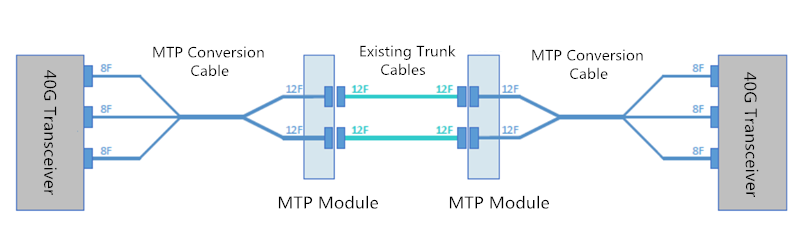
FS MPO/MTP fiber cassettes are available with FHX series and FHD series, which is used for our FHX and FHD fiber optic patch panel respectively. FHD series MPO/MTP cassettes are pre-terminated and pre-tested enclosed units. MTP modular cassettes serve to transmit small diameter ribbon cables terminated with MPO connectors to LC or SC interface used on the transceiver terminal equipment. The fan-outs incorporate LC, SC connectors insert into adapters on the front side of the cassette and MPO connectors plugged into MPO adapters mounted at the rear of the cassette. One or more MPO fan-out assemblies can be installed inside the cassette to connect up to 24 fibers. Alignment pins are pre-installed in the MPO connector located inside the cassette. These pins precisely align the mating fibers in the MPO connectors at either end of the array cables that plug into the cassettes. MPO/MTP cassettes can be deployed quickly and easily in high-density applications, leveraging rack space and fiber enclosure design flexibility. The cassette is interconnected with a high-density fiber optic cable assembly for quick connection to remote or data center applications.
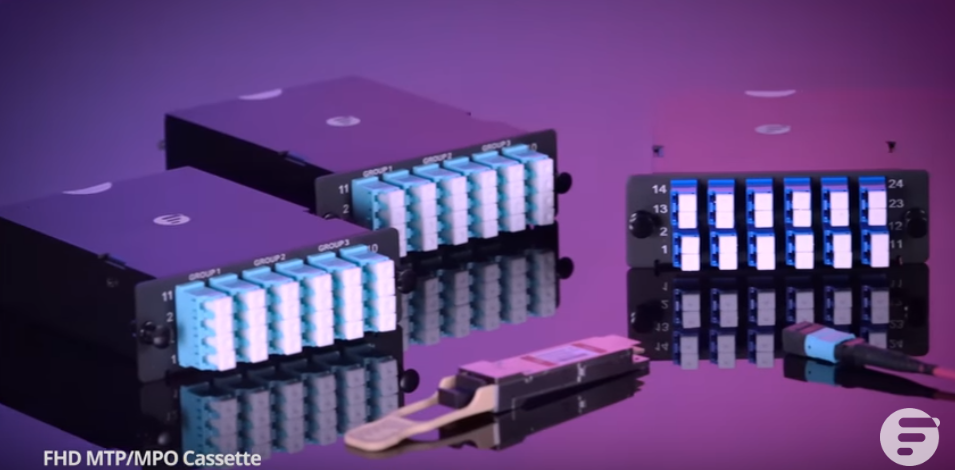
Types of FHD MPO/MTP Cassettes
FS FHD MPO/MTP cassettes are available in different types. To sum it up, there are about 23 diverse products, which can be generally classified from three aspects: fiber count, connector type, polarity type.
Fiber Count
As a pre-terminated fiber product, FS FHD MPO/MTP cassettes are equipped with 8 fibers, 12 fibers or 24 fibers.
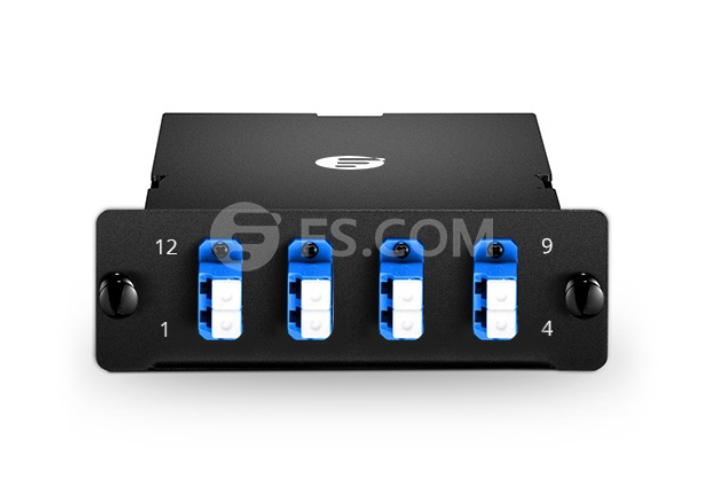
Base-8 MTP Fiber Cassette
Base-8 MTP fiber cassette is designed to upgrade existing LC links to SR4 parallel optics without wasting any of the fibers inside the cable. With respect to the Base-8 connectivity, LC port layout adhere to 1-12, 2-11, 3-10, 4-9 array connections. This Base-8 MTP fiber cassette is ideal to deploy a Base-8 connectivity solution for use in main, horizontal and equipment distribution areas.

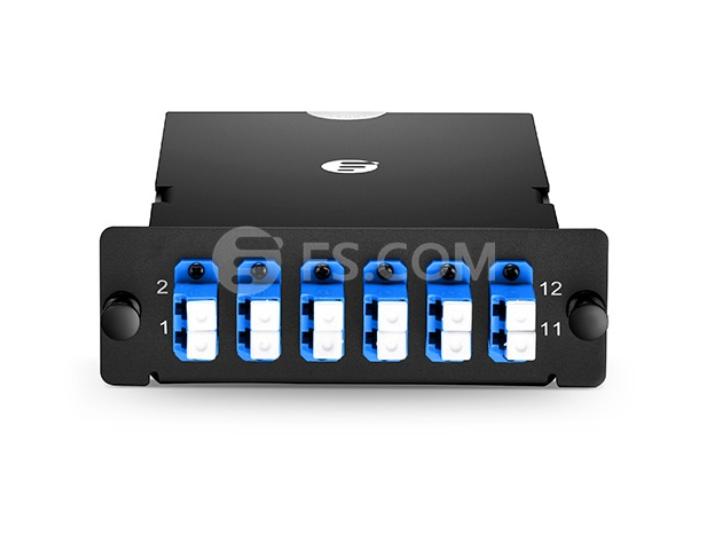
Base-12 MTP Fiber Cassette
Base-12 MTP fiber cassette has 12-fiber MTP adapter on the rear of the units and duplex LC adapters on the front patch field. With respect to the Base-12 connectivity, LC port layout adhere to 1-2, 3-4, 5-6, 7-8 array connections. It’s designed to interconnect with high-density fiber cable assemblies for quick connection of remote or data center applications.

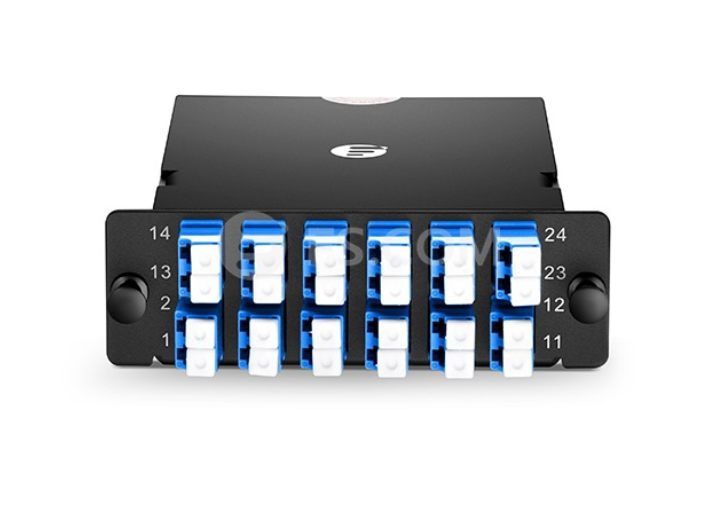
Base-24 MTP Fiber Cassette
Base-24 MTP fiber cassette is similar to Base-12 MTP fiber cassette, except it has 24-fiber MTP adapter on the rear of the units and duplex LC adapters on the front patch field. It has the same array connections from 1-2, 3-4 to 21-22, 23-24. And it’s also designed to interconnect with high-density fiber cable assemblies for quick connection of remote or data center applications.

Connector Type
MPO/MTP cassettes have several different front connectors and rear connectors. There are two kinds of front connectors, such as LC/SC duplex with UPC polished multimode front connector and LC/SC duplex with UPC/APC polished single mode front connector. And also two rear connectors, such as MTP/MPO adapter(s) with male ferrules (pins) and UPC polished multimode rear connector and MTP/MPO adapter(s) with male ferrules (pins) and APC polished single mode rear connector.
Polarity Type
Considering polarity type, there are four types of FHD MPO/MTP cassettes: type A, type AF, type B1 and type B2. Different types of MPO/MTP cassettes transmit different signals and connect with different receiver equipment.
Base-8 Series MPO/MTP Cassettes
The Base-8 series MPO/MTP cassette has no polarity. The specific fiber sequence structure is shown below.

Base-12 Series MPO/MTP Cassettes
There are four different 12/24 Fibers MTP/MPO cassette modules: Type A, AF(Pair Flipped), B1 and B2.

Base-24 Series MPO/MTP Cassettes
There are two different 24 Fibers MTP/MPO cassette modules: Type A, and AF(Pair Flipped).

FHD MPO/MTP Cassettes Installation Steps
When we’re trying to install a FS FHD MPO/MTP cassette, we can follow the installation steps below to complete the equipment.
- Insert the cassette through the mounting bracket and secure it by locking the plastic rivets.
- Feed one end of the cassette patch cord through a desired grommet location and connect it to the rear port of the cassette.
- Route and connect the free end of the cassette patch cord to the appropriate equipment.
For more installation methods, please check out the video below.
Conclusion
FHD series MPO/MTP cassettes are used for inter connector or cross connector connectivity when the distance between two devices is too long. They’re dominant in high-density data centers for their reliable interface, optimized performance and minimized server rack space. FS.COM provides various popular cassettes, such as 1xMTP (8-Fiber) to 4xLC duplex fiber cassettes, 3xMTP (8-Fiber) to 6xLC quad cassettes, 1xMTP (12-Fiber) to 6xLC duplex cassettes, 2xMTP (12-Fiber) to 12xLC duplex cassettes and 1xMTP (24-Fiber) to 12xLC duplex cassettes. I’m sure you can find one to satisfy your needs.
Related Articles:
MPO/MTP Fiber Cassette Module Solution
Differences of MTP Cassette Types