Nowadays, with high speed communication networks evolving quickly, great importance has been attached to data security. Network managers must guard against not only non-contact eavesdropping, but also physical intrusion or tapping of the cables. Any of these security threats can result in serious problems or great economic loss. Luckily, keyed LC products can provide the security necessary to limit authorized physical access to the network and prevent inadvertent or malicious access. Maybe you may feel a little surprised at this. How keyed LC products can achieve it? Now let’s get together to know more about the keyed LC connectivity assemblies.
The keyed LC system is a small form factor (SFF) connection system which allows manageable and easily identifiable network segregation by using a range of physically unique keyed connector and adapter combinations. Each color stands for a unique pattern, which ensures that only the same-colored products can be connected to support the data link. With this special characteristics, keyed LC components are perfect for high density networks and can effectively reduce some wrong connections caused by accident mistakes.
There are many kinds of keyed LC connectivity products in fiber optic communication. Each of them has different specifications and applications. And they comprise a range of network equipment to enable deployment of a high performance low loss network. Now, here is a brief overview of these connectivity assemblies members.
Keyed LC fiber optic patch cable, also called secured LC fiber patch cable, is a critical element in the keyed LC connectivity products assemblies. The LC connectors on both ends of the cable have specific color codes and functional keyed features to identify and manage restricted network connections, which ensure the data security at the mechanic level. Keyed LC fiber patch cable should be used with the same colored fiber adapters or fiber adapter panels. Because each color represents a unique keying pattern that only allows matching same color mating. This is how keyed LC fiber patch cable can provide data security for the fiber optic network.
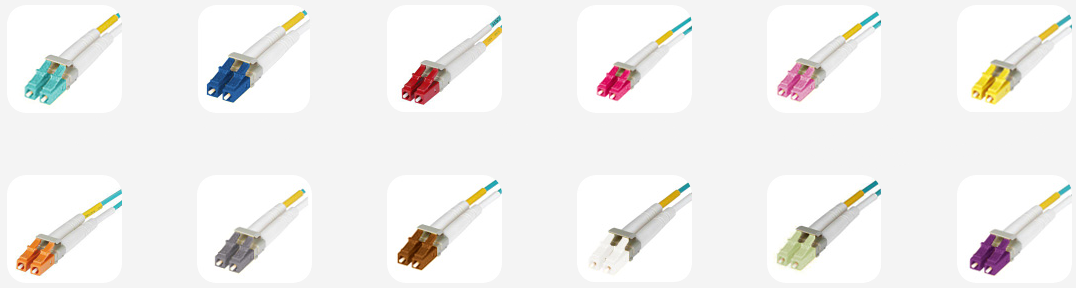
Keyed LC fiber optic adapter has the similar features with keyed LC patch cables. Each adapter is color coded for identification and features a mechanical key, preventing users from accidentally wrong connections. Besides, our keyed couplers utilize a ceramic sleeve suitable for both single-mode and multimode applications. The keyed LC adapters are widely used in Telecom/Datacom, CATV (Community Antenna Television), FTTH(Fiber to the Home), premises distribution and Gigabit applications.

Keyed LC adapter panels with specific color and functional keyed features can identify and manage restricted network cross-connections. Generally, keyed LC fiber optic adapter panels are widely used in restricted fiber cross-connect systems, network-specific backbone and horizontal cross connections.

Keyed LC Cassettes usually support restricted network applications in the data center, equipment room, and telecommunications room. They are designed to prevent unauthorized and inadvertent changes in highly sensitive applications. FS.COM keyed HD MTP/MPO cassettes that have several fiber types provide mechanical security and prevent inadvertent cross connection between MTP and LC discrete connectors.

Of course, except for what I have mentioned above, there are other keyed LC connectivity assemblies such as keyed LC connectors, keyed LC pigtails and so on.
With the application of Keyed LC components, networks can be effectively limited to certain groups, access levels or customers in a co-location environment. This provides an increased level of security and stability by protecting against incorrect patching of circuits. What’s more, there are 12 different colors of the keyed LC products available in Fiberstore, you can build a satisfied keyed LC system by choosing what you like here.