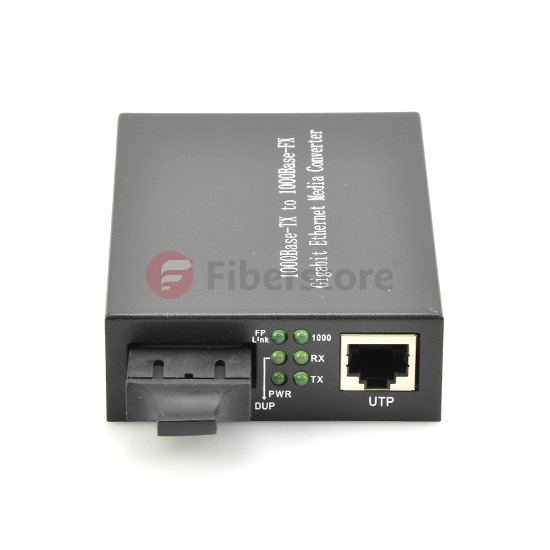
Many devices in the optical communication field are sharing similar functions, such as fiber SFP module and fiber media converter. They are designed as the equipment for photoelectric conversion. Some of you may get confused about the two seemingly similar devices. Don’t worry, in this article, we are going to reveal the secret between SFP fiber module and fiber media converter. In the beginning, let’s go over the definitions of them.
What Is the Fiber SFP Module
The SFP (small form-factor pluggable) module, also called mini GBIC (gigabit interface converter), is a compact, hot-pluggable optical transceiver used for both telecommunication and data communication applications. It converts electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa. Usually, the SFP module consists of optical SFP and copper SFP. And the type depends on whether their SFP ports connect with fiber optic cables or copper cables. The fiber SFP module can support SONET, Gigabit Ethernet, Fiber Channel, and other communication standards.
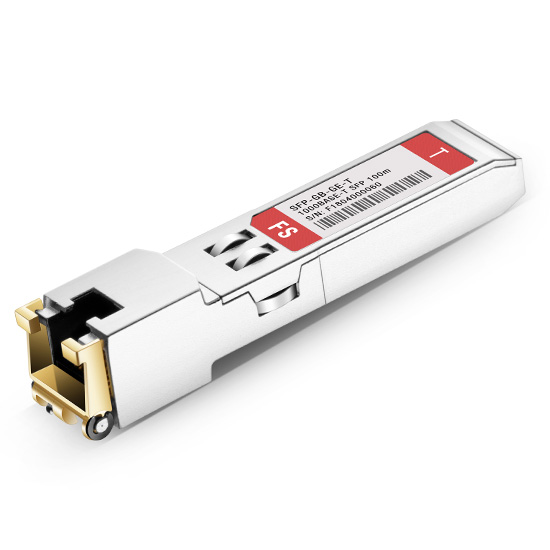

Figure 1: SFP Copper RJ45 100m Transceiver
What Is Fiber Media Converter?
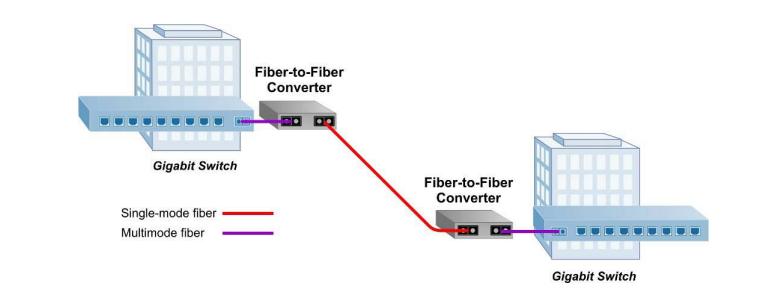
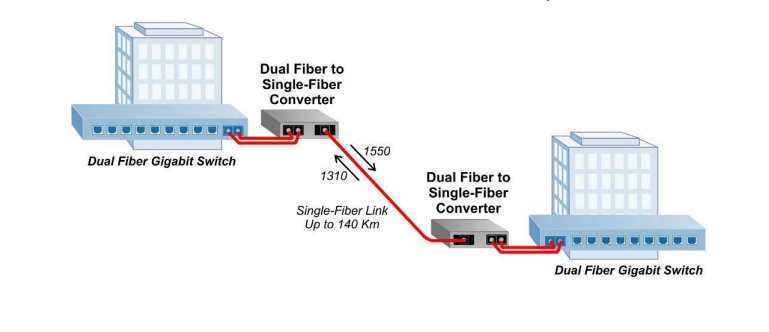
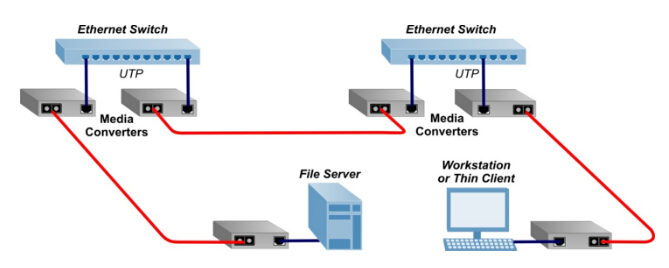
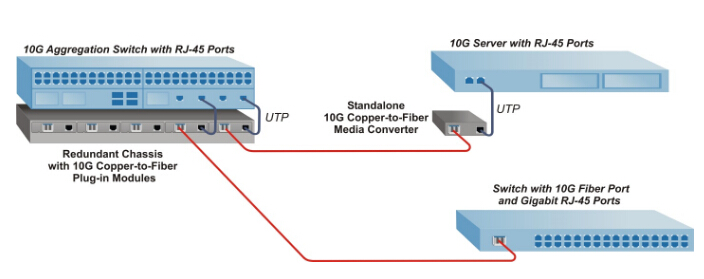
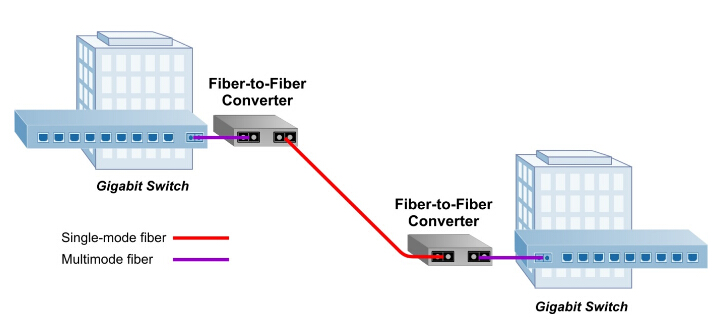
Similar to the working mode of optical transceivers, the fiber media converter receives data signals from one media and transmits them to another. Conventionally, fiber media converters can support two kinds of conversion: copper-to-fiber and fiber-to-fiber. Copper-to-fiber media converters are devices designed to connect two dissimilar media types, such as the twisted pair with fiber optic cabling. They will be chosen when the transmission distance of two network devices with copper ports need to be extended via fiber optic cabling. When it comes to the fiber-to-fiber conversion, it supports a connectivity not only between multimode fiber and single mode fiber but also a dual fiber link and single fiber using Bi-directional (BIDI) flow. Conversions between different wavelengths can also be achieved by some fiber-to-fiber media converters.
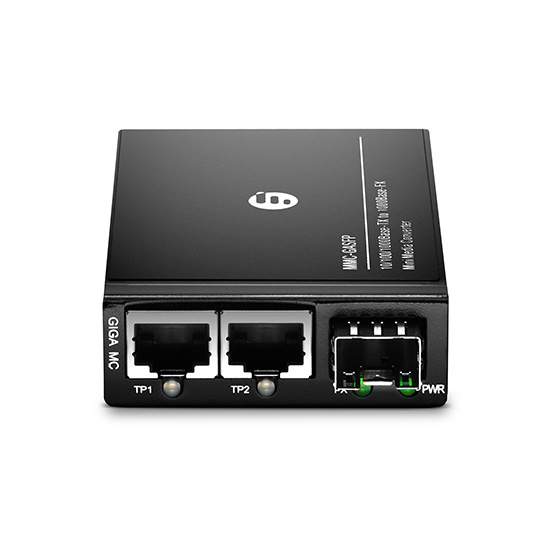

Figure 2: 1*SFP and 2*RJ45 Ports Mini Gigabit Ethernet Media Converter
Connection: Fiber SFP Module vs Fiber Media Converter
A fiber SFP module has a much smaller size than a fiber media converter. Before catching the connection between fiber SFP modules and fiber media converters, we had better know the media converter’s physical structure in advance. So far, copper-to-fiber media converters cover two types of ports. One is for copper (usually the RJ45 port) and the other is for fiber. As for fiber ports, two kinds can also be found. One is designed to insert fiber optic transceivers (SFP, XFP and etc), and the other to connect fiber optic patch cables (SC, LC and etc). As for fiber-to-fiber media converters, both the input ports and output ports are for fiber link. It can be a fiber optic connector for fiber patch cables or an SFF connector for optical modules. After knowing the media converter’s physical structure, it will be easier for us to grasp how does it coordinate with the SFP fiber module. Therefore, if you want to make an SFP module and a media converter both into use at the same time, you need to choose a fiber media converter with fiber ports for an optical transceiver. That is to say, you can insert you SFP module into one side and connect an RJ45 copper cable with the copper port on the other.

Figure 3: 1SFP+1RJ45 Ports Mini Gigabit Ethernet Media Converter
Conclusion
To sum up, in this article, we introduce what the fiber SFP module and the media converter are. Then after studying the media converter’s physical structure and how it coordinates with the fiber SFP module, we can understand the connection between the fiber SFP module and the media converter.