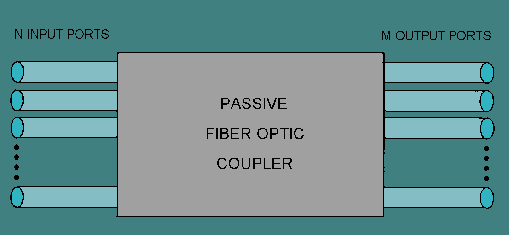
Optical coupler is the extremely important component in a number of phonics devices and systems that couple or split light through wave-guides or fibers. Fiber optic couplers can be either active or passive devices. The difference between active and passive couplers is that a passive coupler redistributes the optical signal without optical-to-electrical conversion. Active couplers are electronic devices that split or combine the signal electrically and use fiber optic detectors and sources for input and output.
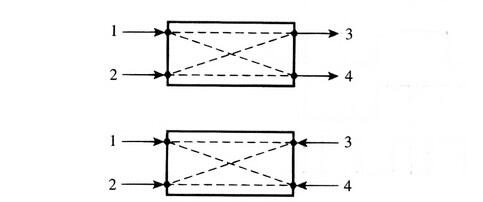
A basic fiber optic coupler has N input ports and M output ports (showed in the above picture) which typically range from 1 to 64. But generally, they are four-port devices and their operation relies on the distributed coupling between two individual waveguides in close proximity, which results in a gradual power transfer between modes supported by the two waveguides. The brief principles of four-ports fiber optic coupler is given in the following picture. If light enters into the port 1, it will be splitted into the output ports between ports 3 and 4. And port 2 functions in the same way. And sometimes, one of port 1 or port 2 is unused, so the fiber optic coupler will act as a Y or T coupler (Y or T stands for the form of transmission route).
As we have known before, fiber optic coupler can couple or split light, so it also can be called fiber optic splitter. In fact, splitter is named for the function of the device, coulper named for its working principle. These days, the most popular types are fused fiber optic couplers and planar lightwave circuit (PLC) splitter.
Fused fiber optic coupler is a kind of fiber optic couplers, which is formed based on fused biconical taper (FBT) technology. Therefore, it is also known as FBT coupler. It can work on three different operating bands such as 850nm, 1310 nm and 1550nm.
Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Splitter is designed to manage the power of optical signals through splitting and routing. It can provide reliable light distribution and is based on planar lightwave circuit technology. Compared with FBT fused coupler of lower cost, PLC splitter has wider operating wavelength range which is from 1260 nm to 1620 nm, and wider temperature range from -40ºC to +85ºC, better uniformity, higher reliability and smaller size.
Currently, fiber optic coupler is widely used in that it can support FTTX (FTTP, FTTH, FTTN, FTTC), passive optical networks (PON), local area networks (LAN), CATV systems, amplifying, monitoring system and test equipment. As a result, fiber optic coupler with good quality is required. Fiberstore can offer you various kinds of fiber optic couplers with good quality, including fused fiber optic coupler and Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Splitter. For more information, you can visit Fiberstore.