For anyone who wants to know fiber optic cable core, it’s a must to know the structure of a fiber optic cable. For a fiber optic cable, it consists of three basic parts: the core, the fiber optic cable core cladding, and the coating layer outside the cladding.
What Is Fiber Optic Cable Core?
A conventional fiber optic cable core is a glass or plastic made cylinder running along the fiber’s length. This part is designed for light transmission. Therefore, the larger the core, the more light that will be transmitted into the fiber. As we mentioned before, the core is surrounded by the cladding layer to provide a lower fiber optic cable core index of refraction. So more light can be transmitted into the fiber.
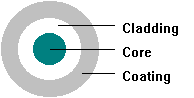
Figure 1: the structure of the fiber optic cable
Fiber Optic Cable Core Types
According to different standards or features, the fiber optic cable can be grouped into different types. For example, classified by connectors, we can get LC fiber, SC fiber, etc; classified by transmission mode, we can get multimode fiber and single mode fiber. Likewise, with different features, the fiber optic cable core can also be divided into different types.
According to the material, plastic and glass cores can be found. When the core is made from pure glass, the cladding is from the less pure glass. Glass type has the lowest attenuation over long distances but comes at the highest cost. As for the plastic core type, it is not as clear as glass one but is more flexible and easier to handle. Moreover, the plastic type is more affordable for us.
Based on sizes, the fiber optic core can be grouped into quite a lot of types. Basically, the most common core sizes are 9 µm in diameter (single mode), 50 µm in diameter (multimode), 62.5 µm in diameter (multimode). For your better understanding, please look at Figure 2 as below. It’s a comparison of the three common sizes when they are inside the same cladding layer diameters (125 µm).
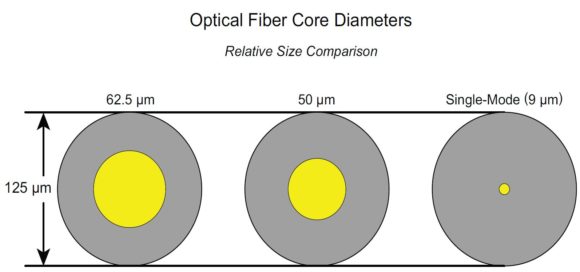
Figure 2: A comparison of optical fiber core diameters
Featured by how many cores in fiber optic cables, two kinds of cable cores can be arranged: the single core and the multicore. The single core type refers to the fiber cable that consists of a core and a cladding layer, which is the most common type in the market. However, the multicore fiber optic cable means that in the same cladding layer, there are more than one core in it. The commonly used cables are four, six, eight, twelve, twenty-four cores.
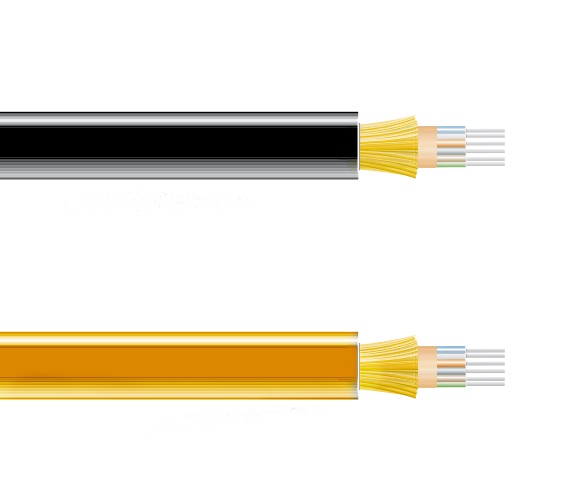

Figure 3: Multicore fiber cable
Conclusion
Based on the knowledge about fiber optic cables, we have a basic idea about its structure and functions each part has played, especially the fiber optic cable core. After knowing what the core is, we also introduce the types of the fiber optic core. Classified by different features, such as core material and size, we can get different types. Hoping after this article, you will have a much clearer vision about the fiber optic core.