Buying fiber optic cables has been a daily thing in our life. Since the field of fiber optic network is still unfamiliar to most people, not to say the detailed information about the fiber optic cable. In this article, we are going to provide some tips for you to buy fiber optic cables. Before that, let’s go over the background information of the fiber optic cable for your better understanding.
What Is the Fiber Optic Cable
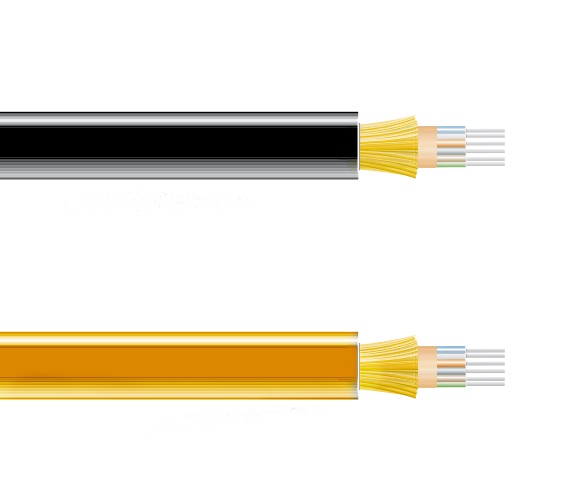
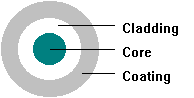
The fiber optic cable refers to a kind of telecommunication cable, containing one or more glass or plastic made optic fibers, usually slightly wider than a human hair. It can carry light to transmit data. Designed for long distance transmission from hundreds of miles to thousands of miles, the fiber optic cable is an ideal choice for networking, telecommunications and storage applications in wiring closets, distribution frames, gateways, central offices and data centers.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
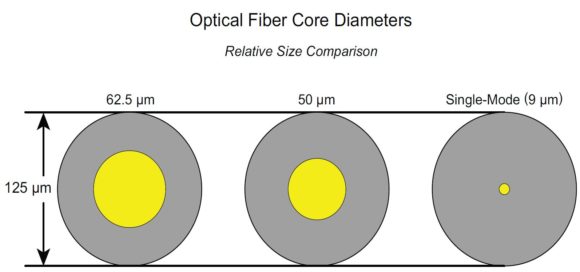
According to different standards or features, there are different types of fiber optic cables. Basically, based on different transmission modes, the fiber optic cable can be grouped into two types: single mode fiber and multimode fiber.
The fiber optic cable for this type is a single strand of glass fiber with a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns, which is narrower than the multimode fiber. Under such a condition, the beam of light is transmitted in a much tighter space with a higher transmission rate. Therefore, it makes the long-distance communication, sometimes as far as between continents more available.

Figure 1: Single Mode Bend Insensitive Fiber Optic Cable
Compared with single mode fibers, the multimode fiber has a larger diameter (62.5µm or 50µm), allowing more space to generate and collect light. Considering about multimode fibers’ transmission performance, it is mostly used for communications over short distances no longer than 2000 m, such as within a building or in a small campus.

Figure 2: OM1 Multimode Fiber Optic Cable
Tips on Buying Fiber Optic Cables
After an overview of fiber optic cables, it’s time for us to learn how to buy fiber optic cables. There are some major steps offered to follow with.
Firstly, preparation. For anyone buying fiber optic cables, they need to have a full preparation. On the one hand, you need to know your network environment, such as the required transmission speed, distance etc. On the other hand, you need to have a basic understanding of the features of all kinds of optic cables. As we mentioned above, there are many types of fiber optic cables available in the market not only just based on different transmission modes, for example, according to different connectors, there are LC fiber, SC fiber, etc. Therefore, you need to know which type suits your network environment.
Next, you need to have a budget for buying optic cables in your mind. There are so many fiber optic cable suppliers in the online market, almost every supplier will offer a different fiber optic cable price. After that, you can begin your online searching. When you browse the product, you can make a comparison of the fiber optic cable price per meter among different suppliers. Besides, you have to check the suppliers’ reputation making sure their service and products are reliable.
Last, but not least. Some buyers buying fiber optic cables for their company need to consider more carefully for their complicate requirements. You had better buy your cables from suppliers who are also manufacturers, such as FS.COM, one of the top fiber optic cable manufacturers. Their service will be more mature, reliable and professional, especially for their after-sale service.
Conclusion
Buying fiber optic cable is not so difficult as you have thought. After reading this article, we believe things will be different for you.