Ethernet cables like Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat 6a are widely used to connect devices on local area networks such as computers, routers and switches. In most successful connections with Ethernet cables, keystone jacks that connect a device to a network port play an important role. But nowadays a new type of keystone jack is also very prevalent. That’s toolless keystone jack. This article intends to introduce the basics and benefits of toolless keystone jack.
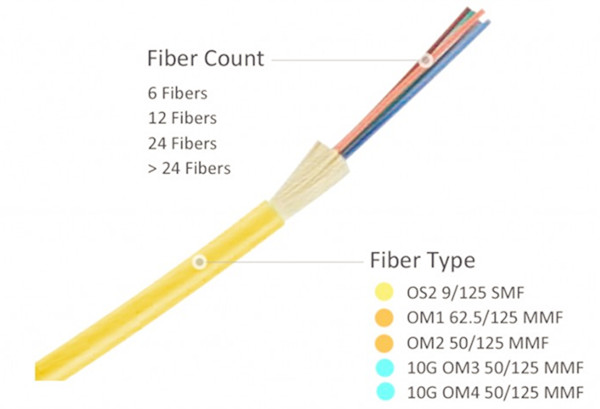
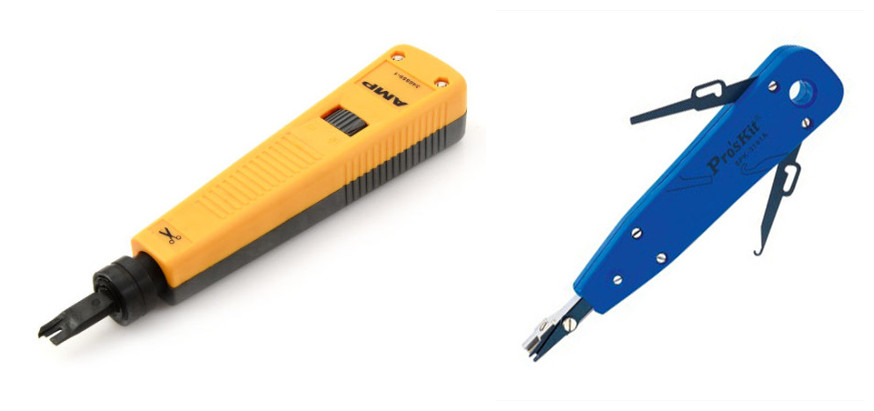
People who have electrical cable installation experience know clearly what is a keystone jack. A keystone jack is a female connector for mounting a variety of low-voltage electrical jacks or optical connectors into a keystone wall plate, face plate, surface-mount box or a patch panel. Keystone plug is a matching male connector, usually attached to the end of a cable or cord. Traditional keystone jack needs a punch down tool to help finish cable installation, but this toolless keystone jack is different. With the snap-fit cap design, conductors can be terminated simultaneously when the cap is pressed into place, allowing for a simple installation without the need for a punch down tool. The most commonly used one is RJ45 (8P8C) toolless keystone jack.

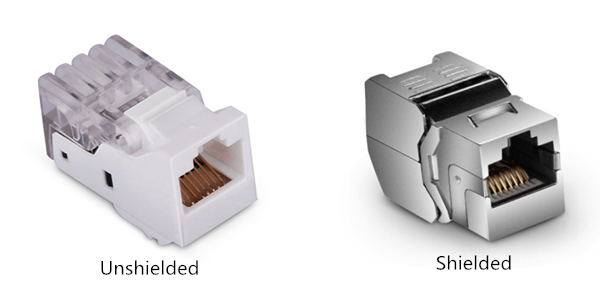
There are shielded and unshielded toolless keystone jacks in the market. The difference between them is whether there is a shielded STP cover outside that is designed for protection from external radiated noise. Choosing a suitable keystone jack should be based on the cables you’re connecting to. In a word, toolless keystone jacks are an ideal solution for terminating and connecting network cables.
Compared to common keystone jacks, toolless keystone jacks have more benefits.
Easy termination. As have mentioned above, there is no need to use punch down tools in the termination process. Except that, simply insert the wires according to the color coding and press down the cap. Termination will be done. Besides, all eight wires can be terminated at a time when the cap enclosed.
Easy Installation. Flexible mounting tab allows installation from front or rear of face plate and secures module into the face plate. Besides, 568A and 568B color wiring diagram is integrated on the outside for quick identification and easy installation.
Save cost. If you do not want to invest a punch down tool for only a time installation, this keystone jack would be a perfect choice.
Convenient to verify proper wiring (only for the unshielded keystone jacks). The snap-fit cap has a large window for viewing terminations. Once the termination is done, you can check whether there is an error occurring to make sure a successful connection.

Using tools to terminate cables is time-consuming, especially under some conditions where time is the paramount factor to be considered. Of course, toolless keystone jacks do not suitable for all cases. It should depend on the practical situation. Here is a simple installation instruction for toolless keystone jack termination.
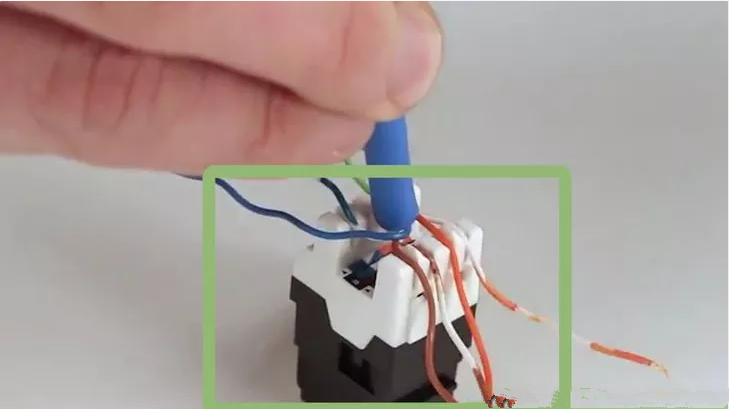
Step one. Trim the end of the Cat6 cable with a crimping tool. Strip off the jacket to expose approximately one inch of wires. This step is similar to the termination process with RJ45 connectors.
Step two. Untwist wires and flatten them as much as possible to make preparation for the next step.
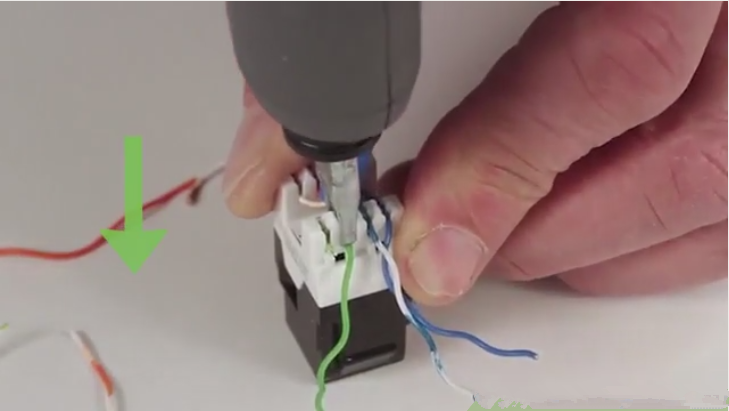
Step three. Just open the top cap, place the wires on the jack according to the color coding on the outside.
Step four. Close the top cap to snap firmly on the plug. In order to ensure a good termination, you can just insert two pairs wires at a time, then repeat the same operation until all wires are placed well.
Step five. Carefully cut off the wire ends using crimping tool. And check the keystone jack to make sure the wires are terminated well.
Toolless keystone jack provides a simple way to terminate and install Ethernet cables. With its special design, time and money can be saved. They are quite versatile and can be mounted easily into a wall plate, which makes them one of the most common and useful components of data centers and networking.